Introduction
In financial planning and analysis (FP&A), business budgets play a pivotal role, serving as navigational tools across all stages of an organization’s journey. Budgets provide direction for businesses, offering a structured pathway towards their goals. From the dynamic landscape of startups to the intricate operations of small to mid-market enterprises, and the robust frameworks of large corporations, budgets serve as the cornerstone of financial management. They not only help outline financial targets but also serve as benchmarks against which actual performance is measured. In this article, we will be taking a look into the strategic importance of leveraging budget to actual variance analysis as a means to elevate FP&A outcomes, empowering businesses to navigate challenges and seize opportunities with precision and foresight.
Implementing Effective Strategies for Budget Variance Analysis
Despite being an important tool that helps companies stay on track, budgets alone don’t showcase the full picture of an organization’s performance. In order to get the most out of budgeting and ensure financial outcomes are trending in the right direction, businesses need to rely on monitoring the differences between budget predictions and actual outcomes. This process is often referred to as budget variance analysis.
Comparing budget vs. actuals allows finance leaders to assess the organization’s performance against their predicted forecast and course correct as needed. In this article, our experts will cover everything you need to know about FP&A variance analysis to help your financial team follow Financial Planning & Analysis best practices and serve as strategic decision influencers for your entire organization.
What is Budget vs. Actuals Analysis?
Put simply, this is an analysis of how a business’ budgets compare with the actuals of real performance.
When an organization’s CFO and other business leaders dive into the financial metrics that help them run the business, understanding the relationship between the anticipated budget and the outcomes that actualize is critical in breaking down all key metrics. In a cyclical process – usually occurring on a monthly, quarterly, and annual basis – FP&A teams use insights and financial models to predict expense and revenue line items. These predictions are called “budgets.”
Once budgets are in place, watching the real numbers that come through as a result of business performance must be done carefully. The “actuals” are then compared to the budget that was put in place in a multitude of financial reporting processes. When an organization has a line of sight to the actual expenses incurred and the actual revenue brought in, its leaders can adjust strategies moving forward to yield even better results.
To nail down the best annual budgeting process and set your business up for success year after year, watch as industry leaders share their thoughts on annual planning in today’s landscape.
What is variance analysis in budgeting?
Finance professionals use variance analysis to assess the actual performance of a business. This type of analysis also allows organizations to compare actual figures to the outlined budget from a set period and evaluate the variances between the two.
As a critical component of Corporate Performance Management, budget variance analysis allows an organization to identify the strengths of its business as well as areas of financial underperformance.
Learn more: Ranking the best Corporate Performance Management Software: our top picks for 2023
The process of comparing budget vs. actuals is straightforward. However, assessing the variance is the key step that allows finance leaders to derive actionable insights and use that information to support strategic decision-making among senior management.
By evaluating whether or not a company’s spending and revenue are leading to a negative variance or positive variance, the finance team can then reassess their current budgets and create more strategic forecasts moving forward.
What is Budget Variance?
In a variance report, variances are categorized as either favorable or unfavorable.
When variance is favorable, the revenue is higher than the budgeted amount OR the expenditures are less than the budgeted amount.With an unfavorable variance, revenue falls short of the budget OR the actual cost of expenses is greater than the budget.
Favourable and unfavourable variances are often connected and can be offset by each other.
Several causes may affect an organization’s FP&A variance analysis. These include:
Inaccurate budgeting
Changes in business conditions
Unmet expectations
Customer acquisition
If the gap between budget vs. actuals is continuously too large, it could mean means that the finance team needs to adjust their forecasting process in order to better predict and assess the performance of their organization.
Favourable and unfavourable variances aren’t inherently positive or negative, even though the terms might make you think you so. Variance analysis
Examples of favourable variances
Positive Revenue variance: where actual sales exceed the forecasted revenue from the budget. This indicates higher sales or better than expected pricing.
Labor efficiency variance: where employees take less time to complete tasks than expected, leading to reduced labour.
Direct materials cost variance: where the cost of materials or resources used in production is lower than what was budgeted for.
Fixed overhead spending variance: fixed overhead costs are lower than budgeted for.
Variable overhead efficiency variance: variable overheads are less than expected, suggesting better resource use efficiency.
Examples of unfavourable variances
Sales volume variance: where sales volume does not meet forecast, thereby indicating higher sales or better pricing than forecasts.
Resource or material usage variance: more resources are used in production than forecasted in budgets, suggesting inefficiency or material waste.
Direct labor rate variance: where wages increase to a rate higher than budgeted and so increase labor costs.
Fixed overhead volume variance: where production volume is lower than expected, causing a higher cost-per-unit by spreading fixed overheads across fewer units.
Variable overheard spending variance: variable overhead costs are higher than budgeted for, caused by price or market price increases.
Why is budget variance analysis important?
Favourable and unfavourable variances aren’t inherently positive or negative, even though the terms might suggest so. Variance analysis is performed to identify whatever. Budget variance analysis plays a pivotal role in Financial Planning and Analysis (FP&A), offering invaluable insights into a company’s financial health and helping to understand why a business’s budget deviates from expectations which is crucial for informed decision-making.
By analyzing budget variances, FP&A professionals can evaluate performance against financial goals for specific periods, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually. This analysis goes beyond just numbers; it serves as a compass for strategic financial planning, highlighting whether targets are being met and signaling necessary adjustments. Whether assessing the impact of a new marketing campaign on revenue or identifying overspending in a department due to increased turnover, budget variance analysis provides a comprehensive view of financial performance. Stakeholders, including investors, benefit from this analysis, gaining insight into a company’s operational efficiency and financial stability. Additionally, budget variance analysis isn’t confined to financial metrics; it can also incorporate non-financial factors, such as quantity analysis, particularly beneficial for manufacturing or construction firms.
By embracing the variance analysis cycle and leveraging variance analysis formulas, businesses can calculate budget variances effectively, empowering them to make data-driven decisions and optimize financial outcomes.
Budget vs Actuals: flexible budget and static budget differences
When Finance uses a flexible budget, they are allowed to make changes to the budget if certain assumptions change. Perhaps a new customer is acquired, a large machinery expenditure comes up, or new hiring results in increased HR spending.
On the other hand, when using a static budget, FP&A teams are not permitted to adjust the budget even if assumptions change. These changes can result in different outcomes, especially when conducting a variance analysis.
Why should you monitor variances in Budget vs. Actuals analysis?
Budgeting is a fundamental practice for all financial planning and analysis processes. By analyzing where your business surpassed expectations and identifying KPIs where it fell short, you can then pivot your financial plan in the future. With the company goals in place, the finance executive team can quantifiably calculate business performance and financial health, and inform business leaders on roadblocks, successes, and new opportunities.
Using an FP&A variance analysis allows a company to measure its year-to-date performance and see which initiatives or processes created a favorable variance. Once a budget to actual variance analysis has been performed, senior management can then steer the right actions and make more data-driven decisions to propel the organization onward.
Budget vs. Actual variance formula
There are several steps involved in calculating your budget vs. actual variance analysis. Below are the different steps to consider:
Step 1. Identify the forecasted amount
The first step is to uncover the budgeted amount. In most cases, organizations will use revenue and expenses or income to calculate this number. While traditional budget owners depend on templates or Excel spreadsheets to derive their budget variance analysis, modern FP&A software can automatically consolidate data and conduct these analyses in a fraction of the time using accounting software or other SaaS solutions.
Aside from an organization’s income and expenses, other factors to consider include EBITDA, cost of goods sold, net income, and gross profit.
Step 2. Determine the actual amount
Next, determine the actual results of what is being analyzed. Businesses typically will use a defined period of time, such as on a monthly, quarterly, or annual basis to conduct their analysis.
Step 3. Calculate the variance
A company can choose to calculate the dollar variance instead of the percent variance.
Dollar variance
The formula is as follows:
Dollar variance = actual amount – forecast amount
The other method is to calculate the percent variance.
Percent variance
This can be done by using the following formula:
Percent variance = [(actual amount / forecast amount) – 1] x 100%
Step 4. Derive results
Do you notice a positive variance or negative variance when reviewing results?
With a clear picture of all discrepancies, a finance team can gain an inside look at their organization’s overall financial performance. From there, they can use that information to derive further strategic insights and steer financial planning forward.
Step 5. Create management reports
Once a team has conducted its budget variance analysis, it is time to present that information to senior management, leadership, and investors. In this management and investor report, be sure to include all of the outcomes as well as the drivers so teams can gain a greater understanding of trends, patterns, or new areas of opportunity. Not only does this paint a clearer picture of the overall performance of an organization, but it also supports strategic decision-making to drive growth.
Step 6. Update forecasts
In some cases, these new strategic insights that have emerged from the analytical process may mean that current forecasts need to be altered. If this is the case, be sure to make the necessary adjustments to forecasts or financial models.
As a general rule of thumb, the forecast should reflect an organization’s roadmap. If uncertain market conditions or other factors are causing a wide range of variances, your team may want to consider adjusting forecasts to reflect these shifts.
The Role of Software Automation in Budget vs. Actuals Analysis
For many years, assessing budget vs. actuals outcomes was tedious, time-consuming, and required many manual inputs. However, with next-generation FP&A tools that exist in the finance ecosystem today, much of the process can be automated. Abacum was built to streamline FP&A processes – including budgeting processes – and make the lives of finance professionals less stressful.
With our tool, FP&A teams can see all key performance indicators in one place, benefit from automated budget vs. actuals variance analysis, and highlight critical information for your organization’s leadership teams – and these examples just scratch the surface of what our tool is capable of.
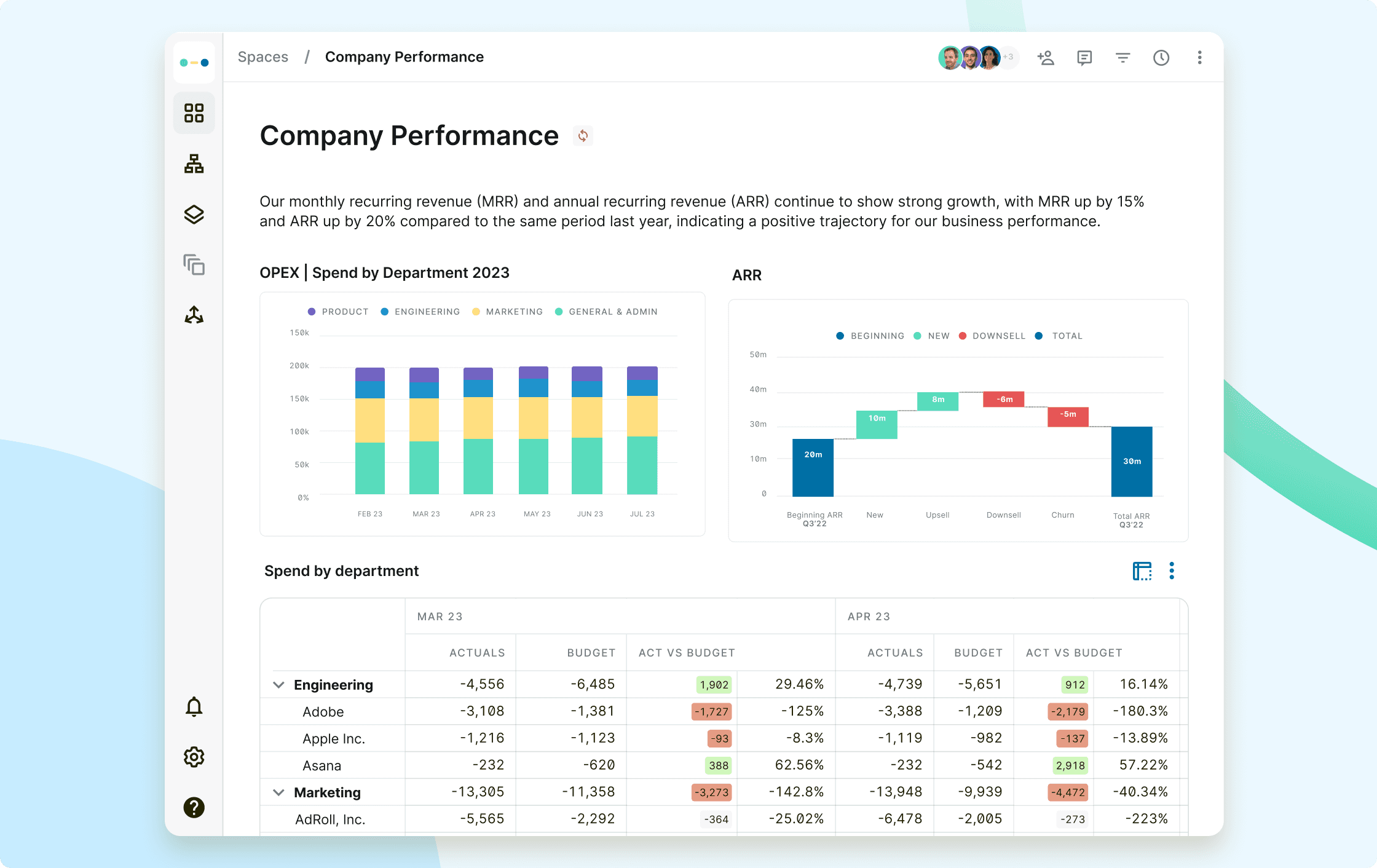
When the actual report comes in during the month-end close process, Abacum pulls the financial data directly from your ERPs and into our system, refreshes all connected reports, and uses impressive visualizations to alert decision-makers of any watch items or red flags. Something that used to take a person hours upon hours to complete can now be done in minutes, freeing up the brightest minds in your organization to absorb the results and make better decisions moving forward.
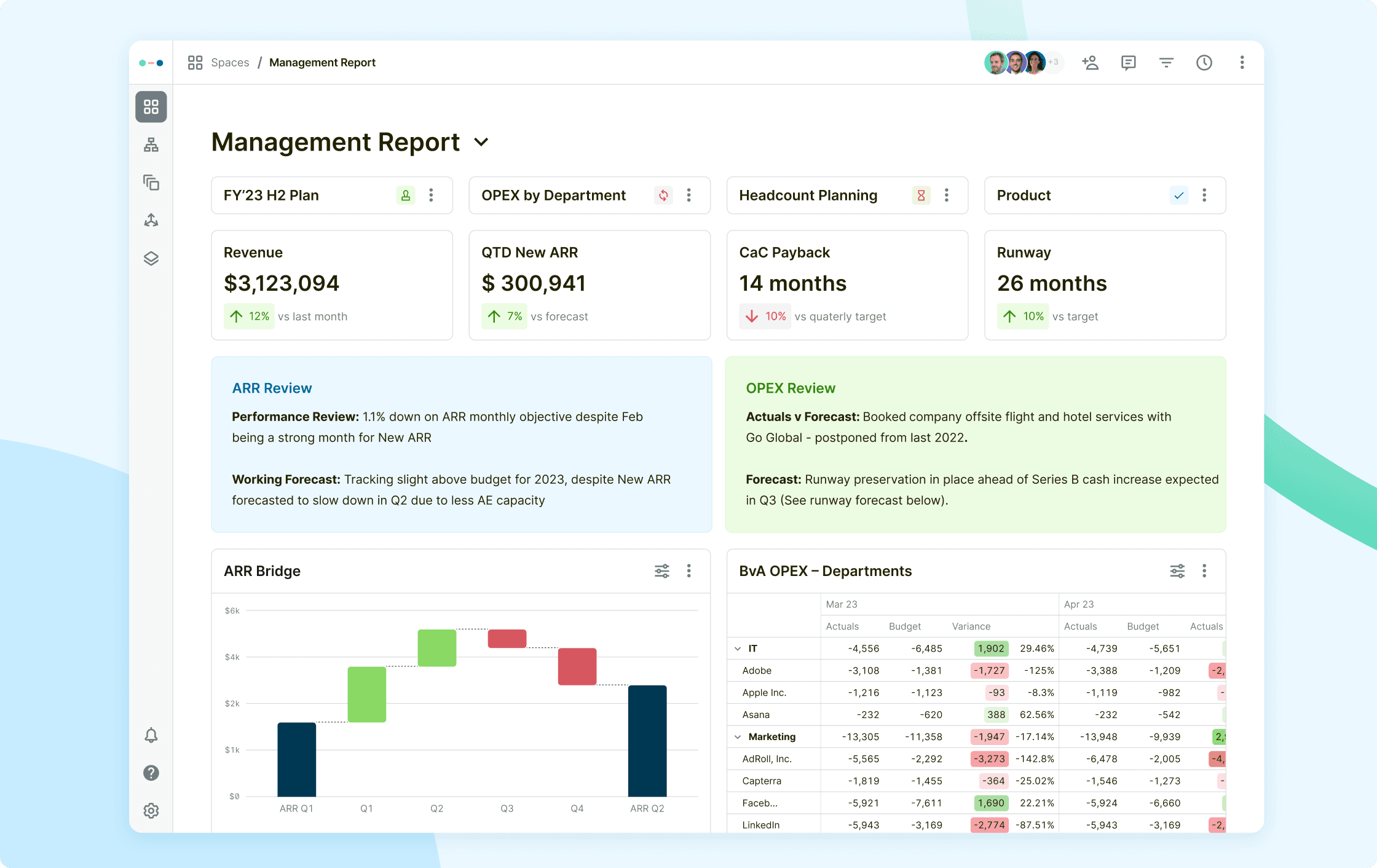
Abacum Tip: We offer a financial planning template for our users – see how it can transform the way you monitor metrics and generate key business reports.
The Benefits of Budget Variance Analysis in FP&A
By embracing the many benefits of this indispensable tool, businesses can navigate the intricate landscape of financial management with accuracy and foresight. Here’s how budget variance analysis empowers organizations to unlock their full potential and drive sustained growth in today’s dynamic market environment:
Performance Evaluation: Budget variance analysis enables a thorough assessment of performance against predefined financial targets, providing clarity on whether goals are being achieved.
Cost Control: By identifying areas where actual expenses exceed budgeted amounts, companies can implement cost control measures to reduce unnecessary spending and improve overall financial efficiency.
Revenue Optimization: Understanding the factors contributing to positive variances in revenue allows businesses to replicate successful strategies and optimize revenue streams.
Resource Allocation: By pinpointing areas with significant variances, you can reallocate resources more effectively, ensuring that funds are allocated with the highest potential for return on investment.
Risk Management: Budget variance analysis helps identify and mitigate financial risks by uncovering areas of overspending, revenue shortfall, or inefficient resource utilization.
Forecast Accuracy: Analyzing budget variances enhances the accuracy of future financial forecasts by incorporating learnings from past performance, leading to more reliable predictions and better resource planning.
Performance Accountability: This analysis fosters a culture of accountability within organizations, as departments and individuals are held accountable for shifts from budgeted targets, encouraging responsible financial management.
Improved Investor Confidence: Transparent and accurate budget variance analysis enhances investor confidence by demonstrating rigorous financial oversight and management, ultimately attracting investment and driving shareholder value.
Continuous Improvement: By conducting regular budget variance analysis and incorporating feedback into financial planning processes, organizations can continuously improve their financial performance and adapt to changing market conditions more effectively.
Integrating Budget vs. Actuals with Financial Forecasting
So how are budget variance analysis and financial forecasting related?
Put simply, budget variance analysis helps an organization create more accurate forecasts for the future. Forecasting is a necessary part of financial planning, which is why it is so important that a finance team makes the necessary adjustments to its models and forecasts on a regular basis.
If you are looking to streamline your budget monitoring and financial analysis processes, consider automating your workflows with the help of a strategic finance solution like Abacum. Unlike Excel spreadsheets that require manual input to conduct analyses, our platform automatically consolidates financial and operational data into a centralized space, allowing finance teams to easily conduct their budget to actual variance analysis and derive fast and reliable business insights.
Find out how to modernize your financial processes and request a demo today.